kompozytor
Bach, Johann Sebastian
tytuł
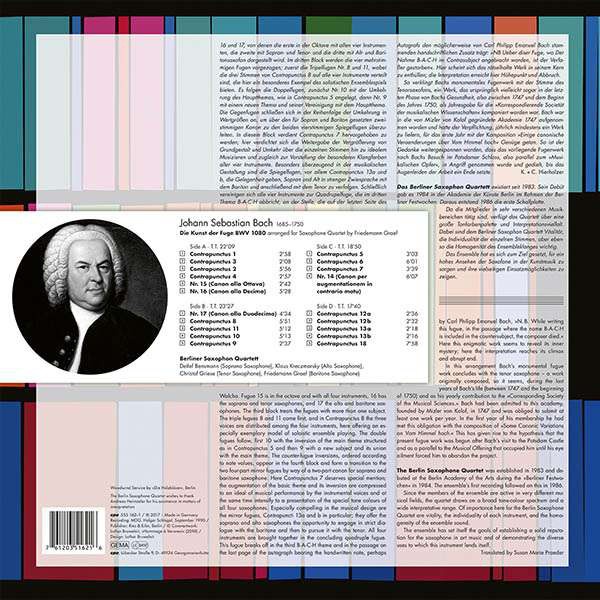
Bach: Die Kunst der Fuge BWV1080 for 4 saxophones
wykonawcy
Berliner Saxophonquartett
nr katalogowy
CPO 555 162-1
opis
Johann Sebastian Bach's "Art of the Fugue", the "summit work of abstract, architectural compositional art" (Edwin Fischer), meets us here in the interpretation of the Berlin Saxophone Quartet in an unusual and unexpectedly delightful form
Bach left the fugue cycle, which was probably begun in 1747 or as late as 1749, without instrumentation instructions and, with a few exceptions, without designations. He also did not complete it, probably due to two eye operations in early 1750 and finally to his death on 28 Vll. of the same year. The only sources we have are the parts of the score in the form of the Berlin autograph (the manuscript of the Prussian State Library and various pages of music in Bach's hand), various proofs of the first printing (presumably to be dated between 1750-53), and a one-page errata list prepared by Carl Philip Emanuel Bach after Smend; documents that had been forgotten until the rediscovery by Wolfgang Graeser in 1924 and a first performance of the work in 1927.
It almost seems as if Bach no longer seemed to care how his last coherent composition, the sum of his entire fugue art, would be sonically realized. Not even the name of the work, added to the autograph by a foreign hand, is authentic. Nor do we know anything for certain about the origin of the varied theme, the time of its creation, and possible relations to the preceding "Musical Offering." Initially, the conviction had prevailed that Bach had written the "Art of the Fugue" for a keyboard instrument, for harpsichord (clavichord) or organ (walcha) (see, e.g. Leonhardt: "Kunst der Fuge, Bachs letztes Cembalowerk"), there have nevertheless been many occasions since Graeser's rediscovery for very different instrumentations, especially in string quartet and chamber orchestra form: the catalog contains the most diverse interpretations, from keyboard instruments, string and woodwind instruments to brass. Bach may have meant all of them or none of them. The only certainty is that the quartet version presented here was not in his imagination, since the wind instrument used here, the "saxophone" after the Belgian instrument maker Adolphe Sax, was not developed until almost 100 years after his death and patented in Paris in 1846.
The listener has the opportunity to judge for himself how suitable the saxophone, or rather the members of the large saxophone family (soprano), (tenor), alto and baritone saxophones assembled in the quartet, are for the representation of Bach's visionary music. Originally conceived by the builder as a bridge between woodwind and brass instruments, the saxophone was soon used in chamber music. An early example is Jean-Baptiste Singelee's 1857 saxophone quartet, but the instrument also found its way into military music and, in the 1920s, into jazz music, where it still plays a central role. As a jazz instrument, it is known to many music listeners. Less familiar is the fact that the saxophone, in addition to its chamber music use, has been effectively employed in concert, opera and ballet literature, for example in Kastner's "Le dernier roi de Juda"(1845), Meyerbeer, Bizet, Massenet or in Debussy (Rhapsody), Glasunov (Concerto in E-flat) and many others, from Prokofieff to Kodaly, Hindemith, Villa-Lobos, Gershwin and Ravel (Bolero). Richard Strauss used a saxophone quartet in his "Symphonia domestica". One can also find examples of independent saxophone quartets. So there can be no doubt that the characteristic sound of the saxophones is perfectly suited to illuminate the polyphonic wonder of the "Art of Fugue". The saxophone quartet, one will note here, allows for a "refreshing new interpretation" (Dümling).
Friedemann Graef (baritone saxophone) arranged the work for saxophone quartet and presents it to the public with Detlef Bensmann (soprano saxophone), Christof Griese (tenor saxophone) and Klaus Kreczmarsky (alto saxophone), encouraged by successes in numerous performances of the work in Berlin, Heidelberg, Frankfurt, Cologne, Bremen, Düsseldorf and Budapest, among others. Friedemann Graef had already set parts of the "Art of Fugue" for saxophone quartet in the early eighties. in 1986 he was commissioned by the Peterskirche in Frankfurt am Main (Cantor Reinhold Finkbeiner) to arrange the complete work, which seemed to him more suitable than any other to trace the lines of contrapuntal polyphony with the voices and the special timbres of the four chosen saxophones and to interpret them in a soloistic and at the same time chamber-musical way.
nośnik
Vinyl
x 2
gatunek
Muzyka klasyczna
producent
CPO
data wydania
04-10-2018
EAN / kod kreskowy
761203516216

(Produkt nie został jeszcze oceniony)
cena 99,00 zł
lubProdukt dostepny w niewielkiej ilości.
Wysyłka w ciągu 3 dni roboczych
Darmowa wysyłka dla zamówień powyżej 300 zł!
Darmowy kurier dla zamówień powyżej 500 zł!
sprawdź koszty wysyłki